
The short answer is that it takes 4 years to become a mechanical engineer.
Why does it take 4 years to become a mechanical engineer?
You’re going to need to go to a 4-year university and obtain your bachelor’s degree to become a mechanical engineer.
In those 4 years, it’s going to be hard work. Do not expect becoming an engineer to be a breeze. You may have to pull some late nights working on engineering projects. You may have to live at school at one period of time. Don’t let anyone tell you that engineering is easy, it’s not.
As a result to prepare you for real life engineering, engineering school is not easy, and it’s not for everyone.
That’s not to say that engineering school isn’t worth it – you’ll get a very comfortable salary and will be set to earn a high paying six-figure income.
Mechanical Engineering is a very high risk, high reward.
You’ll get to work on cutting edge technology and build really cool things such as rockets, spacecraft, aircraft, satellites, turbofans, and so much more.
What is mechanical engineering?
Mechanical Engineering involves the application of using machinery along with engineering principles such as statics, dynamics, and mechanics of materials to solve business problems in real time applications. Mechanical Engineering also utilizes principles such as Thermodynamics, Heat Transfer, and Fluid Mechanics to produce machinery in applications such as turbo pumps, engines, jets, refrigerators and much more.
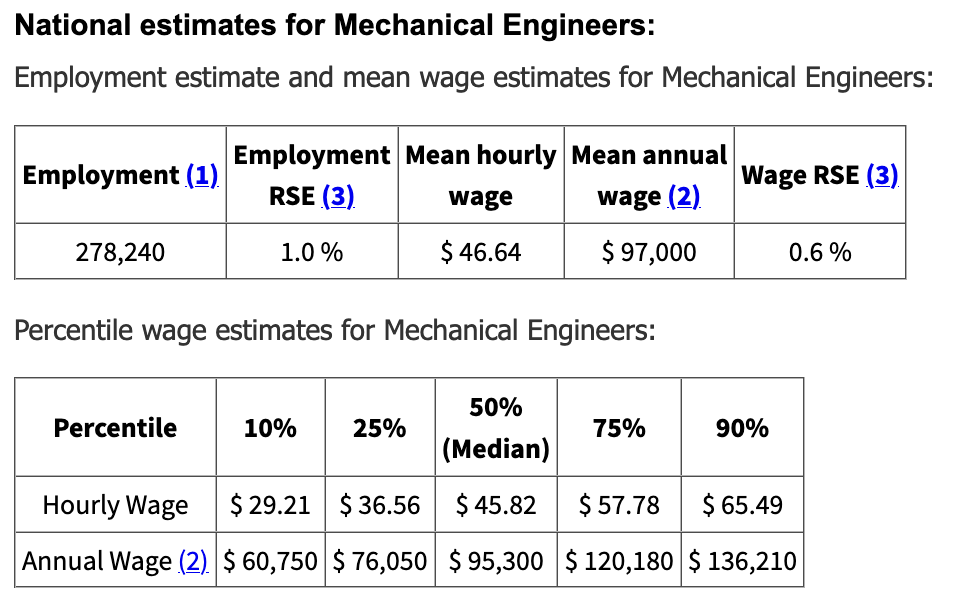
What is the average salary of a mechanical engineer?
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salary of a mechanical engineer is approximately $97,000.
You can also see the percentage breakdown of salaries for mechanical engineers below.
How to become a mechanical engineer
From high school, you’re going to apply to a four year university, and pursue your Bachelor’s in Mechanical Engineering.
In your university studies as a mechanical engineer, you’re going to take courses in classes such as:
- Physics
- Calculus
- Statistics
- Chemistry
- Thermodynamics
- Statics
- Dynamics
- Fluid Mechanics
- Mechanics of Materials
- Heat Transfer
- CAD
- Machining Shop
One of the hardest parts about becoming a mechanical engineer is to go through engineering school and pass all the classes.
During school, you’re going to learn how to craft a resume, interview, and apply for jobs and internships.
If you’ve got good grades, have a solid portfolio of projects, and are involved in engineering memberships as a student, you will have no problem finding a job.
Becoming a mechanical engineer is challenging – see 8 Tips On How To Pass Mechanical Engineering
Why should you become a mechanical engineer?
Mechanical Engineers work in cutting edge technology revolving all things machinery.
If you grew up and enjoyed putting things together and taking them apart, look into mechanical engineering as a career.
Also, if you’re into applications such as cars, formula race cars, off-roading vehicles, mechanical engineering is perfect for you.
Hint – the best mechanical engineers I have met are all passionately into something revolving machinery such as:
- Cars
- Planes
- Trucks
- Off-roading vehicles
- Spacecraft
- Rockets
- Radars
- Satellites
What are some jobs you can get in mechanical engineering?
Design Engineering
Design Engineers utilize CAD in their day to day lives to create mechanical designs for applications to solve customer problems.
They utilize skillsets in the following CAD software:
- AutoCAD
- SolidWorks
- Catia
- ProEngineer / Creo
- Siemens NX
- and tons more
If you want to get a job in design engineering as a mechanical engineer, you will need to learn how to be competent in CAD. The fundamentals of each CAD software are the same, so if you know one CAD software, you know how to use them all. The hardest part about learning how to use different CAD softwares is where the specific buttons that you need to click are based on their functionality.
Design Engineers are responsible for challenges such as ensuring a mechanical component and assembly is geometrically defined and producible. While defining these geometrical requirements, design engineers need to ensure that their parts are mechanically suited for the application.
This means they need to verify that the parts can fit, are strong enough, and they can be made. Although this sounds easy in theory, it’s actually very difficult given real world applications and constraints.
Manufacturing Engineering

Manufacturing Engineers are the bridge between design engineers and an actual finished part. They do all things in the middle and essentially act as the middle man in engineering.
Specific tasks manufacturing engineers are responsible for are:
- Producing build and fabrication plans
- Facilitating manufacturing work orders for parts and assemblies
- Creating assembly sequences for complex mechanical assemblies
- Producing manufacturing bills of materials
- Signing off packages and verifying part fit, form, and function
Structural Engineering

Structural Engineers are responsible for the design and integrity of mechanically engineered components.
They verify mechanical engineering principles and phenomena such as:
- Part acceptance of operating conditions based on yield and tensile strength
- Seismic analysis of buildings, structures, and fixtures
- Fatigue Analysis, Fatigue Strength, Endurance Limit Analysis, Von Mises Stress Criterion
- Verification of rotational part torsional loads
- The strength of mechanical elements
- Screw, Fastener, and Mechanical Connections
Structural Engineering required very in-depth knowledge and understanding of mechanical systems.
They need to be able to understand Free-body diagrams in real world applications. (As all mechanical engineers should)
They also need to understand the concept of various design constraints and connections such as:
- Cantilevered Beams
- Fixed-Fixed Connections
- Pinned-Pinned Connections
- Fixed-Pinned Connections
- Beams On Rollers
And perform respective analyses on those various systems.
This is just a quick summary of what structural engineers do – they are responsible for so much and verifying the integrity of the machine really depends on them.
Test Engineering

Test Engineers are responsible for testing machinery and mechanically designed components.
They utilize destructive and non-destructive means of testing such as:
- Static Testing
- Fatigue Testing
- Dynamic Testing
- Environmental Testing
- Thermal Testing
And analyze the respective results in real time compared to what the structural engineers predict.
Structural Engineers are responsible for the values and certain safety factors that mechanical systems are responsible for, and test engineers are responsible for validating those results in a real world application.
Test Engineers will integrate equipment such as
- Load Cells
- Hydraulics
- Linear Variable Differential Transformers (LVDT)
- Pneumatics
- Pumps
- Compressors
- Fans
- Engines
- Motors
- Actuators
- And much more
To integrate onto specific mechanical test set ups and subject those components to the loads and operating conditions.
Quality Engineering

Quality Engineers are responsible for the incorporation of quality requirements that are set either by the company or the industry for engineers to carry out their work.
They are responsible for actions such as:
- Establishing quality requirements for mechanical components
- Defining what types of documentation and certification are required for mechanical projects
- Handle mechanical defects and non-conformances
- Coordinate requirements between the company and the mechanical part supplier
- Verify mechanical integrity through evaluation of material properties in material certifications
Quality Engineers are also directly involved with destructive and non-destructive examinations to verify mechanical integrity such as:
- Tensile Testing
- Charpy Impact Testing
- Hardness Testing
- Corrosion Resistance Testing
- Ultrasound / Ultrasonic Testing
- Eddy Current Inspection
Closing Thoughts
In 2022 and onwards, the current sentiment overall regarding the job market is much more shifted on tech jobs such as Software Engineering as opposed to more fundamental engineering roles such as Mechanical Engineering, Civil Engineering, and Electrical Engineering.
Although roles in software engineering are compensated very well, they provide a “red-ocean” type of environment. You’re surrounded by sharks and killers and it’s a very competitive environment.
We consider positions in Mechanical Engineering, Civil Engineering, and Electrical Engineering to represent more of a “blue-ocean” type of environment – much more steady and stable.
See a comprehensive guide on how to become a mechanical engineer: How To Become A Mechanical Engineer (Comprehensive)
About the author

Kazuyoshi Fujimoto, PE
Founder | Engineering Career Coach | Principal Mechanical Engineer
Kazu oversees all of ultmeche’s engineering services. He provides consulting such as resume reviews, rewrites, mock interviews, and all services career related. Additionally, Kazu performs consulting work regarding Oil & Gas, Automotive, and Aerospace & Defense. Kazu is licensed as a professional engineer in the state of California and has 9+ years of experience in Oil & Gas, Automotive, and Aerospace & Defense.
